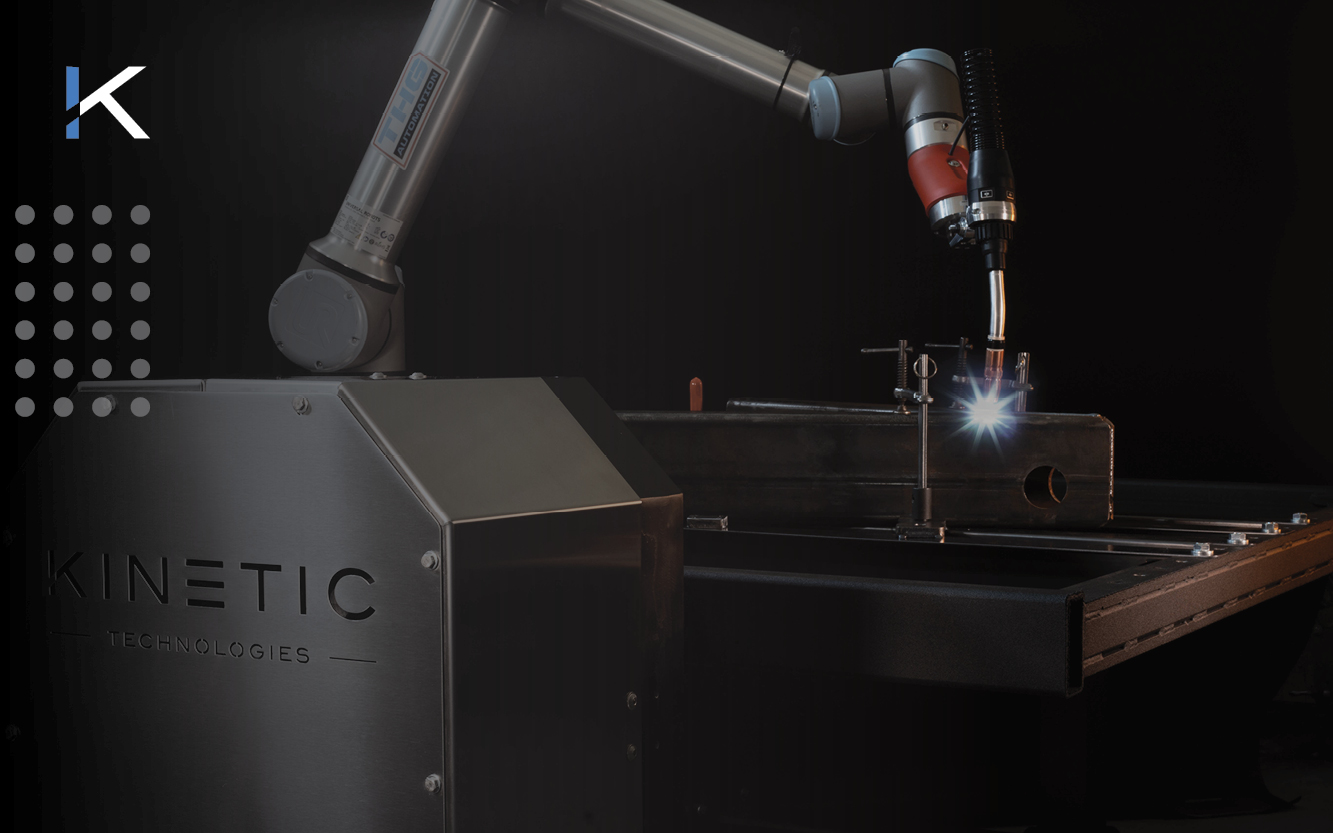
The majority of welding operations are missing a vital component that delivers speed, quality, and cost improvement. What is it?
An integrated welding positioner!
Robotic positioners are an essential component of robotic automation, especially in applications involving robotic welding of large and/or high-volume parts. The positioner has a significant impact on accuracy, repeatability, and overall production quality.
If you’re looking to elevate your production, you’ve come to the right place. Whether you’re already invested in automation or still in the planning phase, make sure you prioritize positioners as much as the robot.
Is a robotic positioner the missing piece for your shop or plant?
This comprehensive guide aims to help robotic integrators like you navigate through these critical choices, unlocking efficiencies you may have never thought possible.
In this article
• How Positioners Boost Productivity ›
• Most Common Types of Welding Positioners ›
• Choosing the Ideal Robotic Positioner: A Guided Approach ›
• The Impact of a Robotic Positioner on Your Operations ›
How Positioners Boost Productivity
Automation delivers increased efficiency and higher production levels. But what you won’t be told is that it’s not just about the robot.
If your positioners are inadequate, even the most advanced robot system will fall short. The solution? Plan ahead and avoid the headaches later.
Welding positioners are specialized devices that securely hold and manipulate workpieces to ensure they are in the optimal position for achieving high welding quality, precise heat input, and easy access.
These devices can smoothly rotate the workpiece along one or more axes, eliminating the need for manual adjustments or setup changes. This capability not only enhances efficiency and precision but also dramatically cuts down on the time and labor invested in the welding process.
Robotic positioners not only elevate productivity but also enable the automation of tasks that would otherwise be infeasible without the ability to rotate workpieces.
Advantages of Welding Positioners
Simultaneous operations: Certain positioners offer the flexibility to mount pieces on opposite sides, enabling multiple robots to perform different tasks at the same time.
Space savings: Contrary to what one might think, using a positioner can actually minimize the floor space required for a robot cell. This proves more efficient than using another type of auxiliary axis and laying out workpieces on separate benches.
Coordinated motion: Positioners allow the part to rotate during the welding operation. This ability reduces cycle time while improving weld quality.
Access difficult angles: Complex geometries often require challenging positions. Welding positioners provide the needed accessibility, making the job easier for robotic arms.
Safety first: Automating the workpiece repositioning process minimizes manual handling risks, making the workspace safer.
Most Common Types of Welding Positioners
Welding positioners vary in type and use. They consist of a working table, rotation motors, speed reducers, an overturning device, an electricity-conducting device, a stander for support, and an electric cabinet that houses the control units. Each component plays a crucial role in the device’s overall functionality.
Some of the most common and effective types of positioners are:
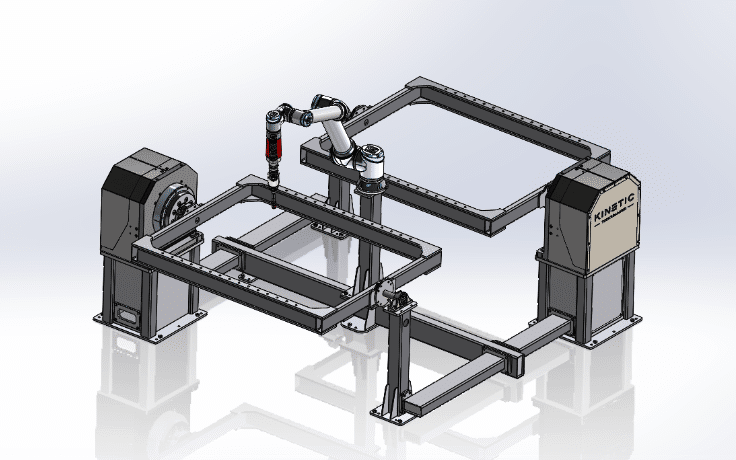
Headstocks/Tailstock Positioners
These are single-axis positioners that excel in placing loads at a 90-degree angle or in a horizontal orientation. They rotate solely on the horizontal axis. The design is especially beneficial for long workpieces like axles and beam structures that need rotation without tilting.
Headstock tailstock positioners can be customized based on production requirements. For example, pair two HSTS positioners together with a robot in the middle to allow two operators to set up and unload parts while the robot works.

Rotary Table Positioner
Featuring a flat spindle at the top with tapped pitch holes, these rotary positioners are perfect for small pieces or heavy and large pieces. The ample, round surface area offers the stability required during the welding process, making them suitable for bulky workpieces.
This kind of positioner excels in accommodating multiple jigs and streamlines the process of loading and unloading workpieces. By facilitating concurrent loading, welding, and unloading activities, it substantially boosts a welding robot’s productivity.
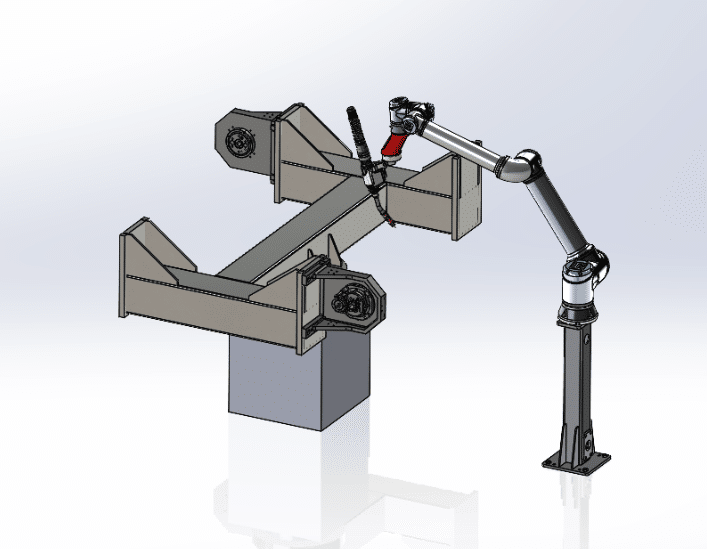
H-Frame Positioners
The H-Frame positioner features an H-shaped structure, enabling a dual workpiece setup. This design offers two distinct zones: one designated for the robotic operation and another for workpiece arrangement by a human operator.
Each component can spin along its horizontal axis, thanks to their placement on a standard headstock-tailstock setup. Both headstock-tailstock units have a ground-based rotational axis, permitting either unit to be presented to the robot for work.
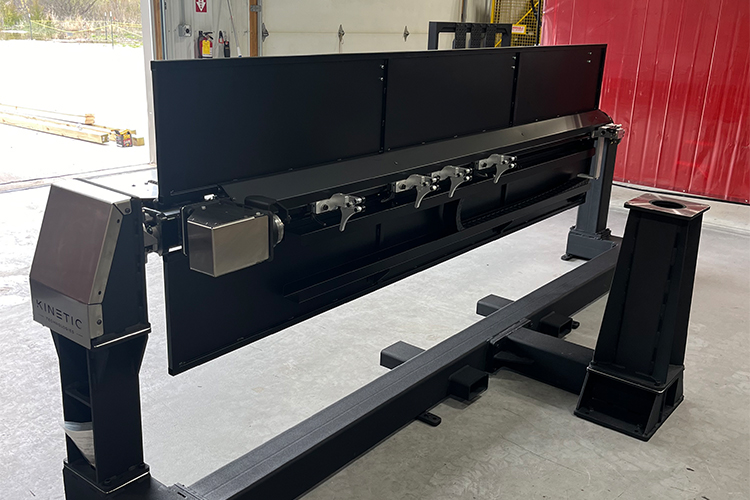

Ferris Wheel Positioners
These positioners stand out for their three-axis range of motion, including horizontal rotation, tilting, and vertical load adjustments. Despite their low profile, which makes loading easy, these positioners offer adjustable settings to suit specific project requirements. Their flexibility makes them a go-to choice for intricate welding applications where multiple axes of movement are beneficial.
Choosing the Ideal Robotic Positioner: A Guided Approach
When choosing a positioner for your operation, consider factors like load capacity, workpiece geometry, and available space. Ask yourself these questions:
Do I need a single positioner or a dual-positioner setup?
If you’re dealing with large or heavy workpieces, consider a dual-positioner setup or even a more complex multi-axis positioner system. Some positioners can handle larger loads but come at a higher cost. Evaluate the trade-offs between system complexity and capability when making your selection.
What is the geometry of my workpieces?
The geometry of your workpieces plays a vital role in the type of positioner you’ll need. For complex shapes, a multi-axis positioner might be more suitable as it can rotate the workpiece in various directions for optimal welding access. Flat or cylindrical shapes might do well with simpler, single-axis positioners.
How much space do I have for the robot and positioner?
Space constraints can significantly limit your options. Some positioners are designed to have a smaller footprint, allowing you to integrate them into tighter spaces. If floor space is a significant concern, look for positioners that offer vertical stacking or other space-saving configurations.
The Impact of a Robotic Positioner on Your Operations
A strategically designed positioner can be the game-changer you’ve been waiting for. The precise control and repeated accuracy afforded by advanced positioners don’t just enhance weld quality; they also contribute to overall process efficiency and cost reduction.
So if you’re on the fence about investing in a robotic positioner, let’s be clear: You’re not just buying a piece of equipment; you’re investing in unparalleled accuracy, control, and efficiency for your operation.
Ready to take the next step?
Kinetic Technologies offers commercially-available, standard products that can link together for ease of scaling an operation. We designed our rotary and headstock/tailstock positioners to be durable and high-quality – making the positioners build to last. Contact us today to find out how you can optimize your robotic welding systems to their full potential.
FAQ
What is a robotic welding positioner?
A welding positioner for robotic welding is a specialized device that holds and rotates the workpiece, giving the welding robot better access to the joints that need to be welded. This improves the accuracy and quality of the weld by allowing the robot to reach challenging angles and positions without straining its mechanical limits.
Are robotic welders worth it?
Absolutely. These machines outperform skilled human welders in both efficiency and consistency. With an efficiency rate of up to 85%, robotic welders dramatically outpace manual welding. Robots never experience fatigue and they don’t require breaks. This ensures a consistent, high-quality weld every single day.
What is the most common problem with robotic welding applications?
One of the most frequent setbacks in robotic welding is burnback, often caused by an improperly trimmed gun liner. To tackle this, always use high-quality liners and trim them according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Contact tip wear can result from incorrect welding parameters or low-quality wire. To prolong the lifespan of your tips, use quality wire and optimize your welding parameters.
What is the best application for robotic welding?
Robotic welding shines in environments where you have high production volumes but low diversity in part types. However, even if you deal with a wide variety of parts, robotic welding can still be a viable option if you invest in the right tooling. The key factor to consider is cost-effectiveness, as specialized tooling can add to the initial expenses. Regardless of volume or variety, the most important thing is to have parts that are simple and uniform. This ensures the robot can consistently perform the weld at the exact same location every time.




